Welcome to BAOLAN EP INC.
24-Hour Hotline
- Carbon Capture Utilization
- VOCs series
- DeSOx-DeNOx-Dedust
- Consumables

Contact Baolan

Address: Jurong East Road, Huantai Industrial Park, Zibo City, Shandong Province
Tel: +86-135-8959-1050
E-mail: [email protected]
Tel: +86-135-8959-1050
E-mail: [email protected]
Paint waste gas treatment
——————————————— ◆ Exhaust gas analysis ◆ ———————————————
Composition of paint exhaust gas
The waste gas from spraying is the waste gas generated during coating spraying. The components of the waste gas from spraying and drying are as follows:
Benzene, toluene, xylene, hexane, heptane, methylethyl ketone, ethyl acetate, carbon tetrachloride, etc., mainly deal with "triphenyls" and volatile organic waste gas (VOCs).

Characteristics of paint exhaust gas
(1) the main components of spray painting waste gas are benzene, toluene, xylene and some dust particles. Most spray painting waste gas also contains ethyl acetate, butanone, isopropanol and some ether substances.
(2) the components in the spraying waste gas have certain complex characteristics, certain toxicity, and are easy to burn and explode. During the treatment, it is necessary to use a high-pressure fan to pump the spraying waste gas into the high-pressure spray tower for pretreatment, then enter the low-temperature plasma equipment to destroy the molecular structure of the organic waste gas, and then enter the washing tower to wash the damaged small molecules and finally empty them.
——————————————— ◆ Technological design ◆ ———————————————
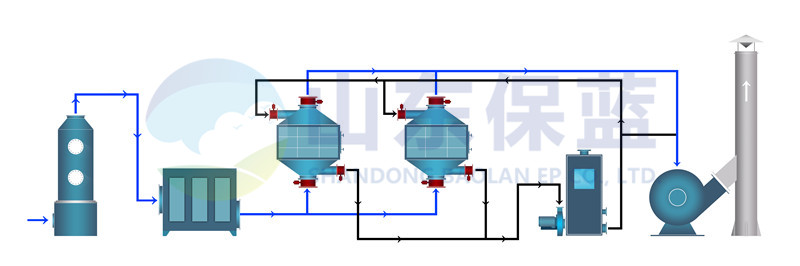
Process Brief
(1) after the dust and granular substances are removed by pretreatment, the waste gas is sent to the activated carbon adsorber I and II. When the activated carbon adsorber I is close to saturation, the treatment gas is automatically switched to the activated carbon adsorber II (the adsorption operation of the activated carbon adsorber I stops), and then the activated carbon adsorber I is desorbed and desorbed with hot gas flow to desorb the organic matters from the activated carbon. In the desorption process, the organic waste gas has been concentrated, and the concentration has increased dozens of times than before, reaching more than 2000 ppm. The concentrated waste gas is sent to the catalytic decomposition unit, and finally discharged as CO2 and H2O.
(2) after the desorption, the activated carbon adsorber I will enter the standby state. When the activated carbon adsorber II is close to saturation, the system will switch back automatically, and at the same time, the activated carbon adsorber II will be desorbed and desorbed, so it will work in cycle.
(3) when the concentration of organic waste gas reaches more than 2000 ppm, the catalytic bed can maintain spontaneous combustion without external heating. The scheme not only greatly saves energy consumption, but also reduces equipment investment because the treatment capacity of catalytic decomposer only needs 1 / 5 of the original waste gas treatment capacity (60000m3 / h). This scheme is not only suitable for continuous work, but also suitable for intermittent work.
——————————————— ◆ Cooperation ◆ ———————————————


Copyright © 2014-2023 BAOLAN EP INC.
Telephone: +86-135-8959-1050 E-mail: [email protected]
Address: Jurong East Road, Huantai Industrial Park, Zibo City, Shandong Province




