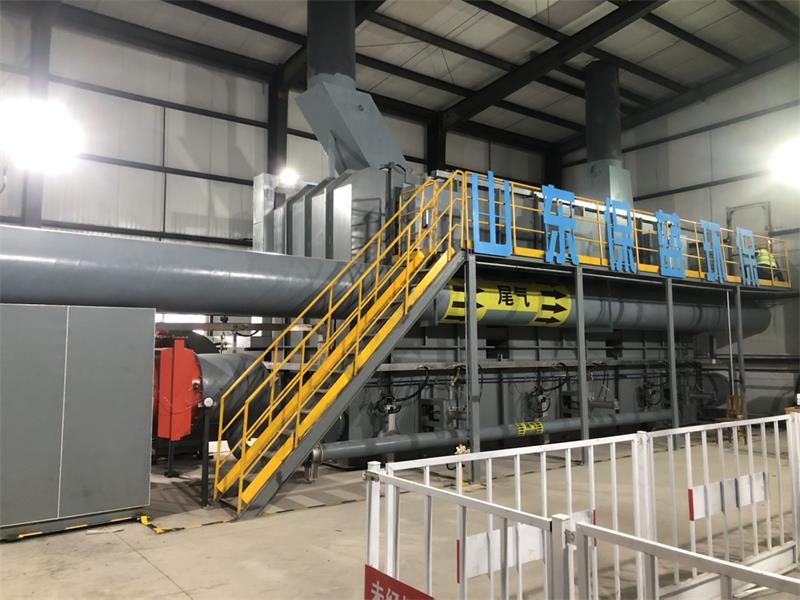
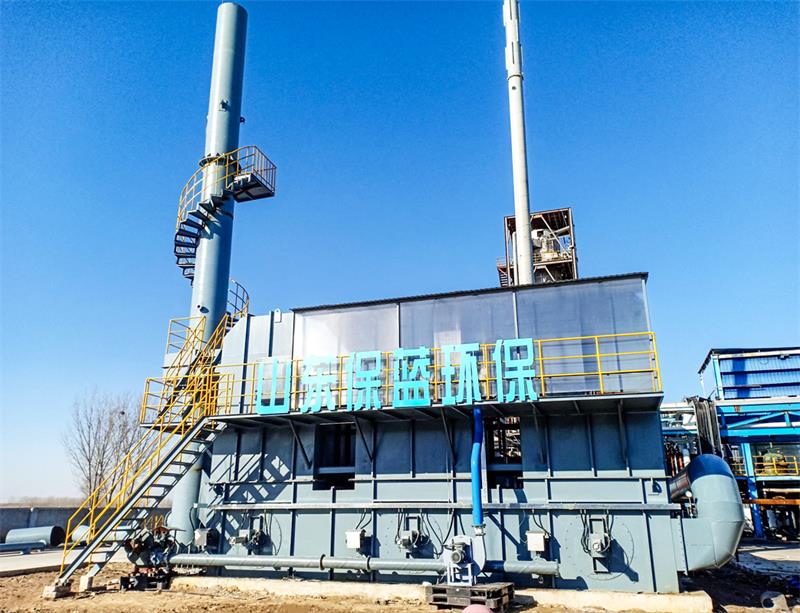
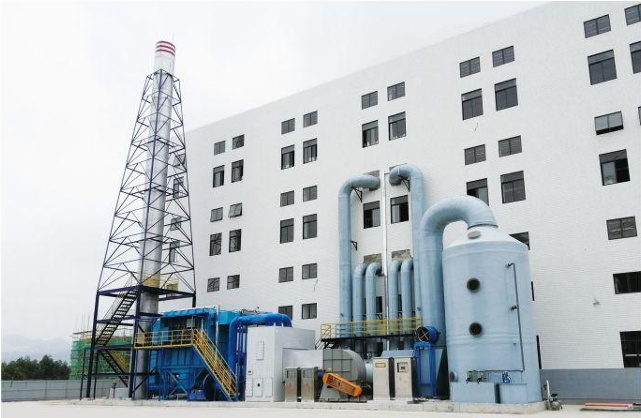
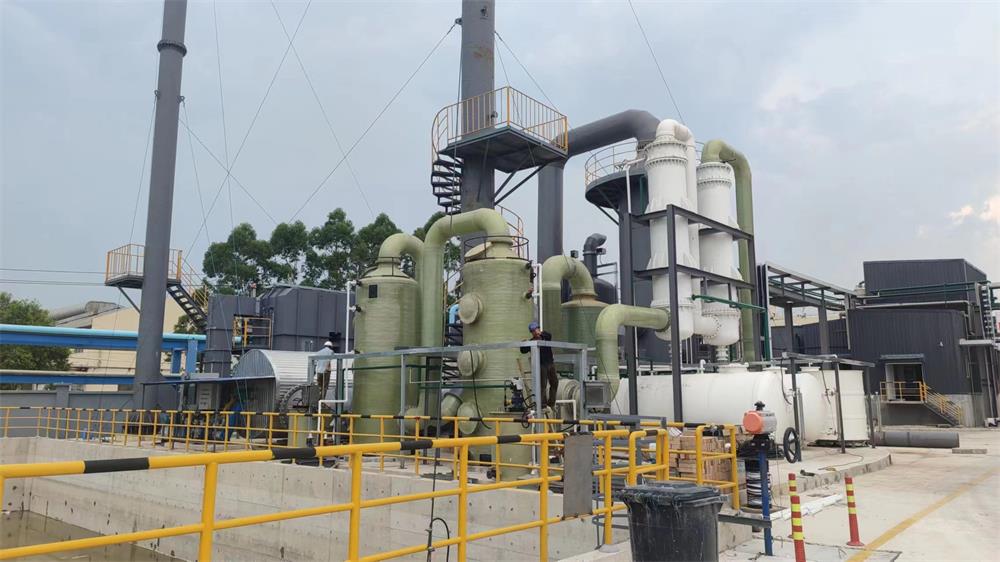
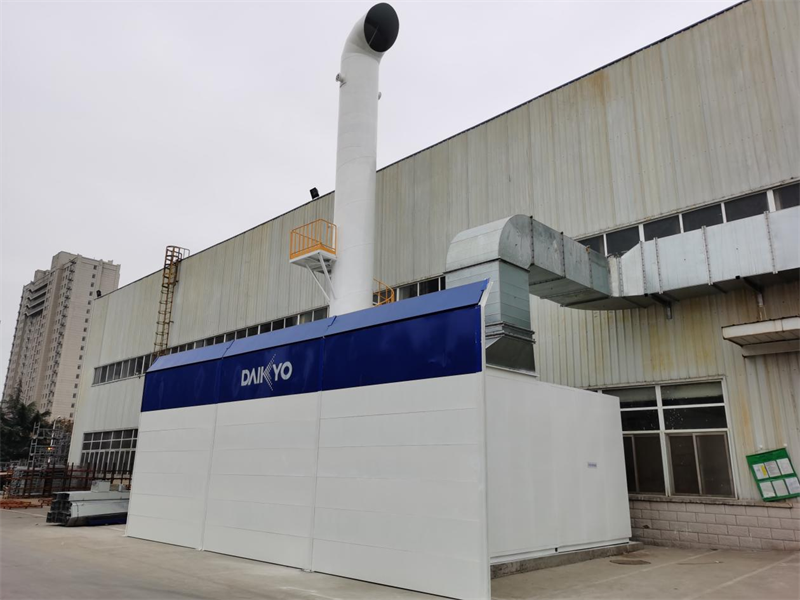
- Product Details
Zeolite Adsorption and Desorption
Technology Introduction
Zeolite adsorption-desorption technology in the treatment of organic waste gases (VOCs) is a highly efficient and mature exhaust gas treatment technology. Its core is to utilize the adsorption characteristics of zeolite molecular sieves to achieve the concentration and recovery/destruction of organic compounds in low-concentration, large-volume waste gases.
The technical principle can be divided into two core stages: the adsorption stage and the desorption stage.
Core Material: Zeolite Molecular Sieve
Before understanding the principle, it is necessary to first recognize its core material — zeolite molecular sieve. It is an artificially synthesized or natural aluminosilicate material with a microporous crystal structure.
Its core characteristics determine the advantages of the technology:
1. High Selective Adsorption: Its pore size is uniform and single-sized (usually between 0.3-1.0 nm), like a sieve, only allowing molecules smaller in diameter than its pores to enter and be adsorbed, while blocking larger molecules outside. For VOCs treatment, hydrophobic zeolites are usually selected, which have weak adsorption for water molecules (kinetic diameter about 0.27 nm) but strong adsorption for most VOC molecules (such as toluene, xylene, etc., usually >0.4 nm in diameter).
2. High Adsorption Capacity: It has a huge specific surface area (up to 500-1000 m²/g), providing a large number of sites for adsorbing pollutants.
3. High Thermal/Chemical Stability: Composed of stable inorganic crystals, it is resistant to high temperatures (up to several hundred degrees Celsius) and acid-base corrosion, which ensures that its structure will not be damaged during high-temperature desorption regeneration, resulting in a long service life.
4. Non-flammability: Compared with activated carbon, zeolite is an inorganic material and does not burn, making it safer when treating some reactive or high-temperature waste gases.
Detailed Working Principle
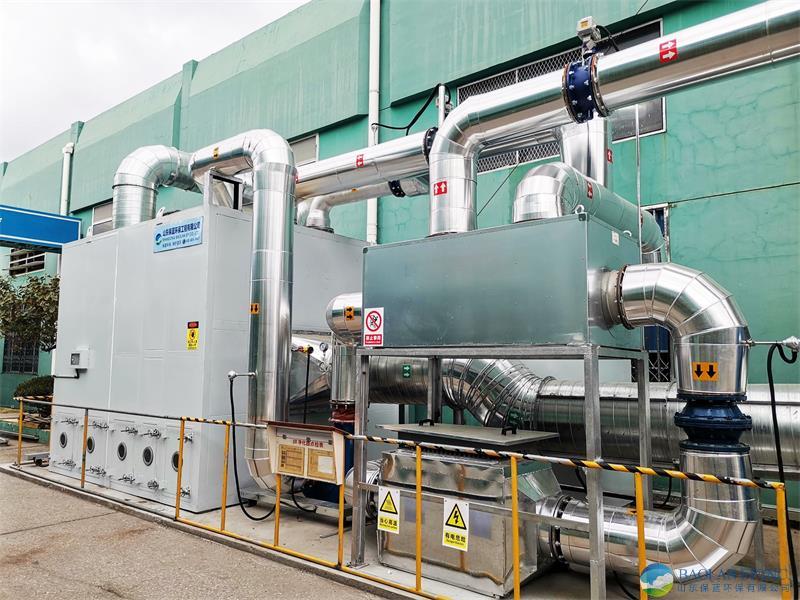
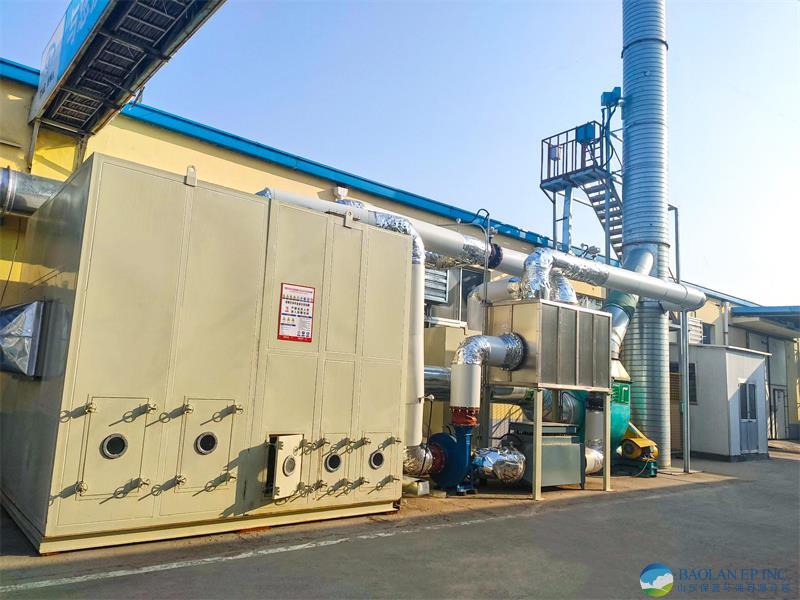
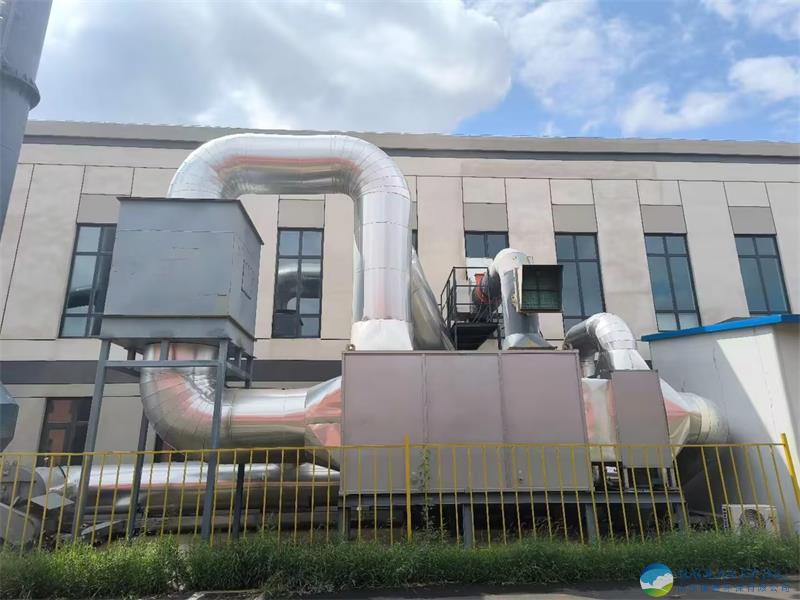
The entire system usually consists of a zeolite rotary wheel (core equipment), heat exchanger, heating device (such as electric heating or gas heating), cooling device, and subsequent treatment equipment (such as TO, RTO, CO, etc.).
Stage One: Adsorption Process
Process Description: Organic waste gas, driven by a fan, first undergoes pretreatment (such as filtration, cooling, etc.), then passes through a continuously slowly rotating zeolite rotary wheel.
Stage Two: Desorption and Regeneration Process
Process Description: A small stream of high-temperature (usually 180~220℃), low-flow hot air (called "desorption air") is blown in reverse into a smaller sector of the wheel — the desorption zone (about 5%~25%).
Stage Three: Cooling and Preparation for Re-adsorption
Process Description: The high-temperature zeolite area after desorption cannot immediately enter the adsorption area, otherwise it will affect the adsorption efficiency. Therefore, the rotor will rotate to a cooling zone, where a stream of clean air at room temperature cools it down to near room temperature.

Final Treatment
The high-concentration waste gas coming out of the desorption zone has the following two main final treatment methods:
A typical TO system usually includes the following main parts:
1. Recovery Method: For solvents with recovery value (such as toluene, ketones, etc.), a condenser can be connected to cool the VOCs into liquid form for recovery. After purification, they can be reused.
2. Destruction Method: The high-concentration waste gas is introduced into a catalytic oxidation furnace (CO), regenerative thermal oxidizer (RTO), or thermal oxidizer (TO) for high-temperature oxidation, completely decomposing it into harmless CO₂ and H₂O. Since the waste gas has been concentrated, the airflow is small and concentration is high, significantly reducing the auxiliary fuel consumption required for incineration, making the operation very economical.
Technical advantages
High Purification Efficiency: Purification efficiency is high, usually reaching 95%~99% or above.
High Concentration Efficiency: Large volume, low concentration waste gas is concentrated into small volume, high concentration waste gas, greatly reducing the investment and operating costs of subsequent treatment equipment.
Stable Operation: Zeolite is heat-resistant and non-combustible; the system operates safely and reliably with a long service life.
Humidity Interference Resistance: Hydrophobic zeolite has weak adsorption of water vapor, suitable for waste gas environments with relatively high humidity.
Continuous Automated Operation: The rotor continuously rotates, with adsorption and desorption occurring simultaneously, enabling unattended operation.
Complete Decomposition: Directly converts organic substances into CO₂ and H₂O, with no secondary pollution (provided that post-treatment is adequate).
Application areas
Especially suitable for large volume, low concentration organic waste gas treatment, such as:
Printing and coating industries
Automotive painting and furniture painting industries
Electronics and semiconductor industries
Petrochemical and pharmaceutical industries










