- Product Details
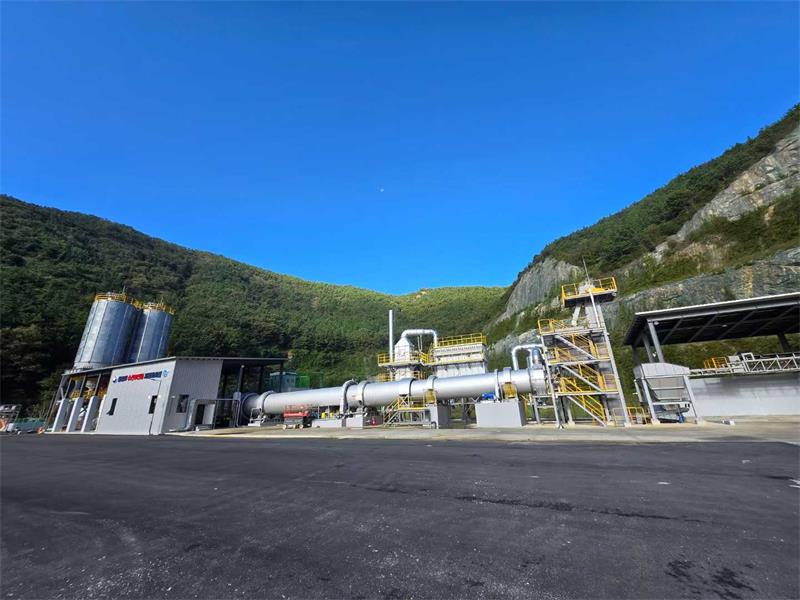
Fluidized Roasting Device
Technology Introduction
The fluidized roasting device is a new type of high-efficiency and energy-saving ro asting device developed by Baolan EP Inc. under the "dual carbon" goals. The basic principle of the device is to use fluidized suspension technology, allowing gases and solids involved in reaction heat and mass transfer to be in a fluid and dynamic state, achieving the fastest mass transfer, heat transfer, and speed, and maximizing energy efficiency.
"Fluidized suspension" involves crushing and grinding the processed solids into fine powder, increasing the contact area between the solid and gas, and shortening the transfer and reaction distance within the particles. The gas flowing from bottom to top through these powders, upon reaching a certain speed, will suspend the solid particles, causing them to move continuously, similar to a fluid, hence the term fluidized suspension.
When the apparent flow rate increases to the initial suspension velocity, the pressure drop across the bed equals the buoyant weight of the particles per unit area of the distribution plate (the weight of the particles minus the weight of the fluid volume they displace). At this point, the particles no longer support each other and begin to suspend in the fluid. As the apparent flow rate is further increased, the bed expands, the pressure drop across the bed remains nearly unchanged, but the movement of particles within the bed intensifies. This stage of the bed is known as the fluidized bed.
When the apparent flow rate increases to equal the free settling velocity of the particles, all particles are carried away by the fluid, and the fluidized suspension process enters the transport stage.
Process Flow Introduction
After roasting, the materials sequentially enter the primary cooler, secondary cooler, tertiary cooler, and quaternary cooler for temperature reduction and cooling. They then proceed to the cooling bed, where air cooling and circulating water cooling reduce the temperature of the materials to 80-100°C, completing the entire process of material roasting.
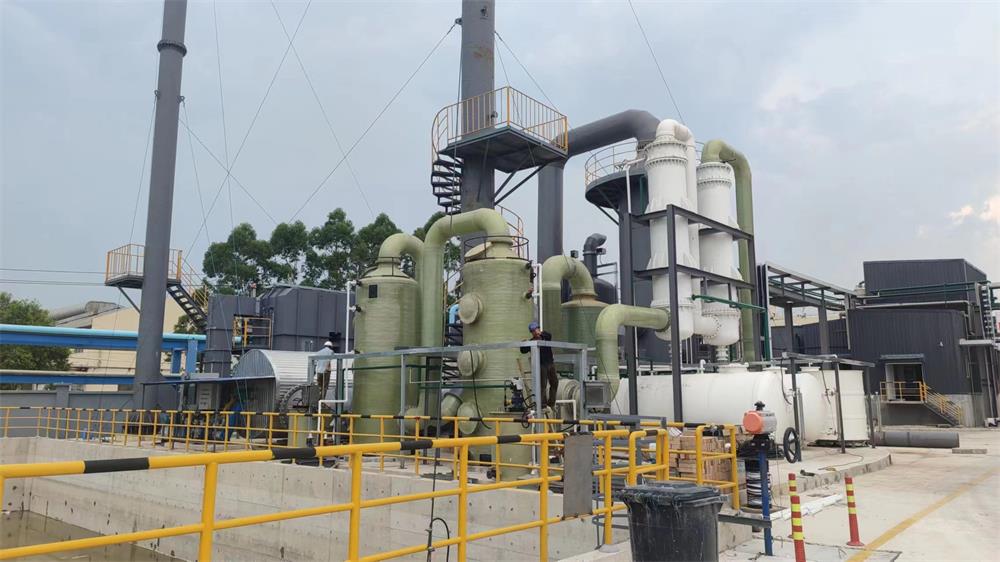
System Introduction 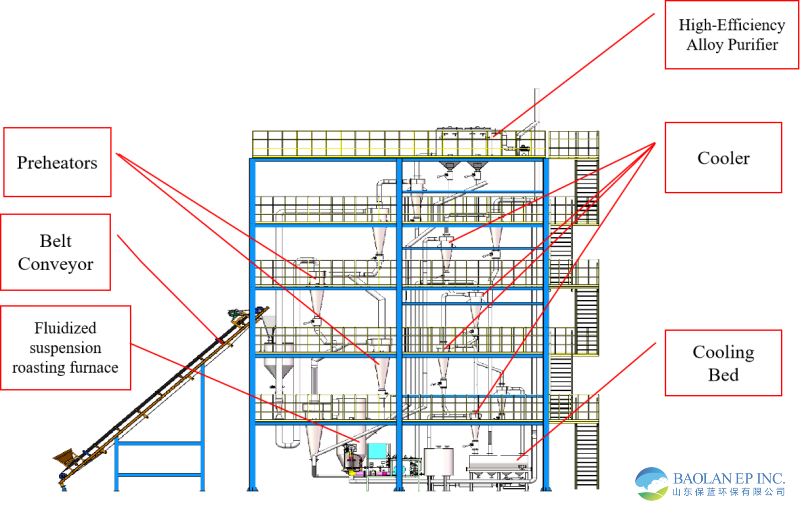
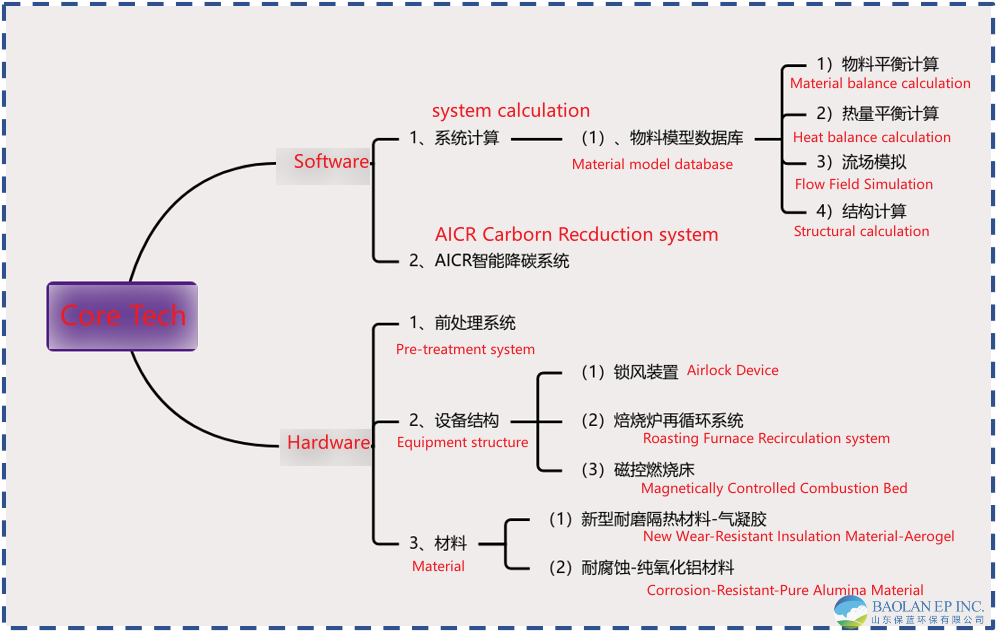
1. Fluidized Suspension Roasting Furnace
The Fluidized Suspension Roasting Furnace utilizes high-temperature hot gases to induce a suspended fluidized motion in the materials on the fluidized bed. The roasting process for the materials is completed in a continuous suspended fluidized state.
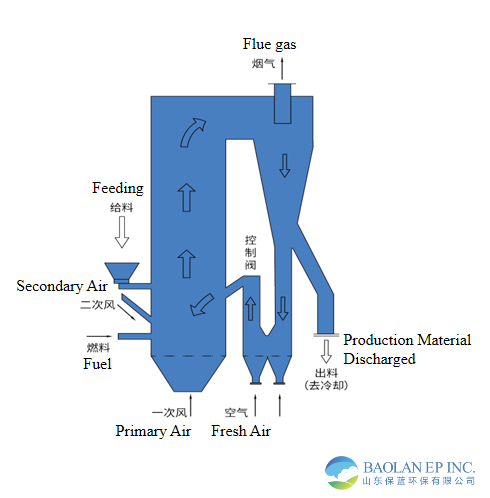
1. The core part of the roasting system consists of a fluidized suspension roasting furnace and preheater. Fuel is injected from the bottom of the roasting furnace, providing heat. The heat carried by the roasted products is cooled and recovered in the preheater by primary air. The heat carried by the airflow in the preheater is used to preheat and dry materials in the preheating drying section and partially dehydrate the crystallized materials, thus recovering heat and reducing energy consumption.
2. Due to the continuous circulation of a large amount of solid materials, carrying a significant amount of heat, the roasting temperature remains uniform. Even in the event of temporary fluctuations in material supply or fuel supply, the temperature in the roasting furnace and preheater remains uniform and stable. The furnace temperature is typically controlled between 850-1250°C.
3. The entire system operates under positive and negative pressure, with air supply provided by a Roots blower. The advantage of this blower is that the air supply volume does not vary with system pressure fluctuations. Even if there are brief abnormal fluctuations in the furnace, the air supply volume remains stable. Roasting temperature is regulated by increasing or decreasing the material feed rate or fuel injection rate to produce the desired quality of product. The roasting furnace has a wide adjustment range, adjustable between 40% and 100%. When production is reduced, the combustion air volume is also reduced, maintaining a low excess air coefficient and thus keeping energy consumption low.
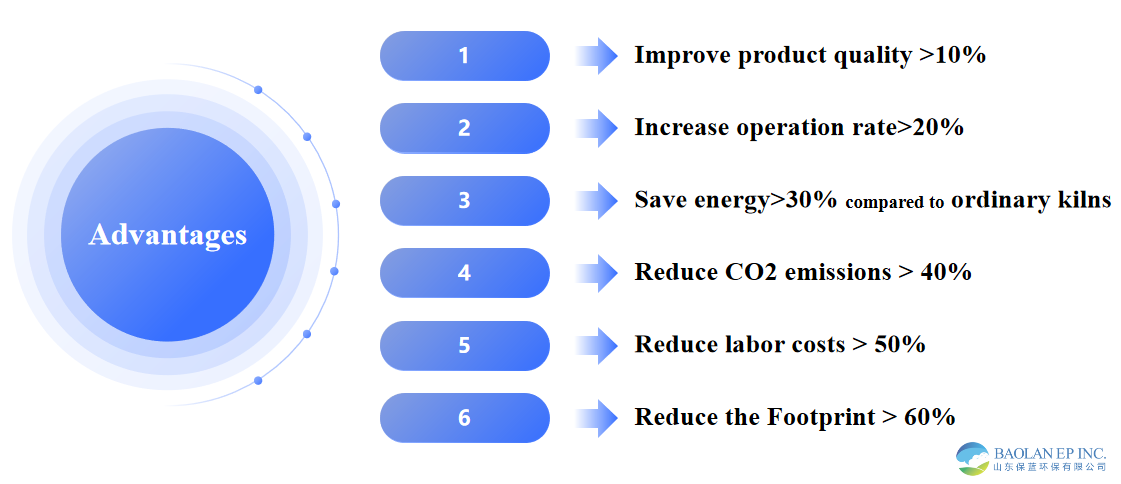
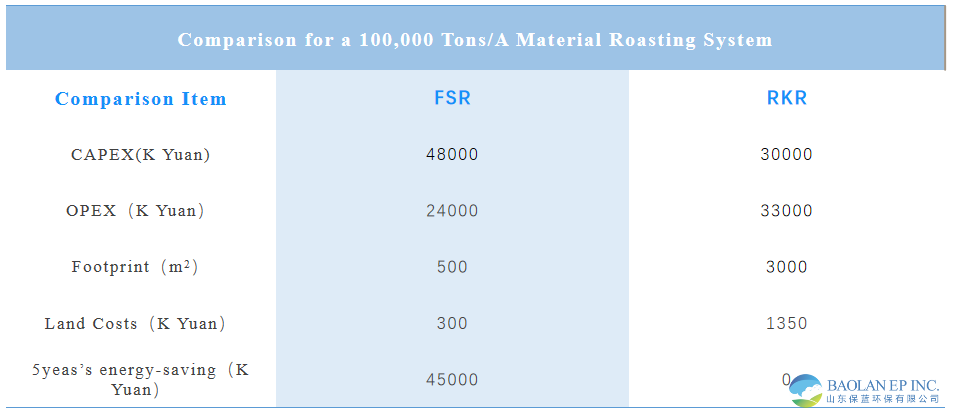
4. The roasting furnace is compactly configured, effectively utilizing space and reducing the footprint by more than 50% compared to a rotary kiln. Its steel structure frame is lighter than other furnace types, and its unit investment is lower than that of a rotary kiln. Due to the lower roasting temperature compared to a rotary kiln, the thermal shock on the inner lining is minimal, resulting in a lifespan of up to 10 years and maintenance costs about 50% of those for a rotary kiln.
2. Cooling Bed
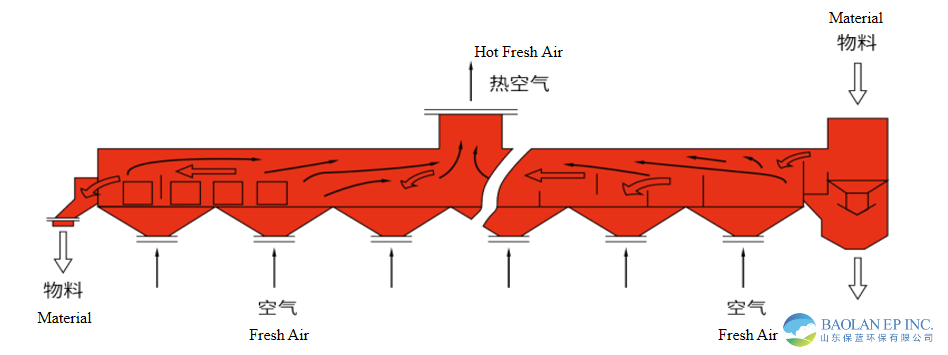
3. Preheating and Cooling System
The preheating and cooling system mainly consists of multi-stage separators before and after the fluidized suspension roasting furnace. The working process of this system is accomplished through the coordinated cooperation of these multi-stage separators. The preheating and cooling are achieved by blowing air to heat or cool the (raw) materials.
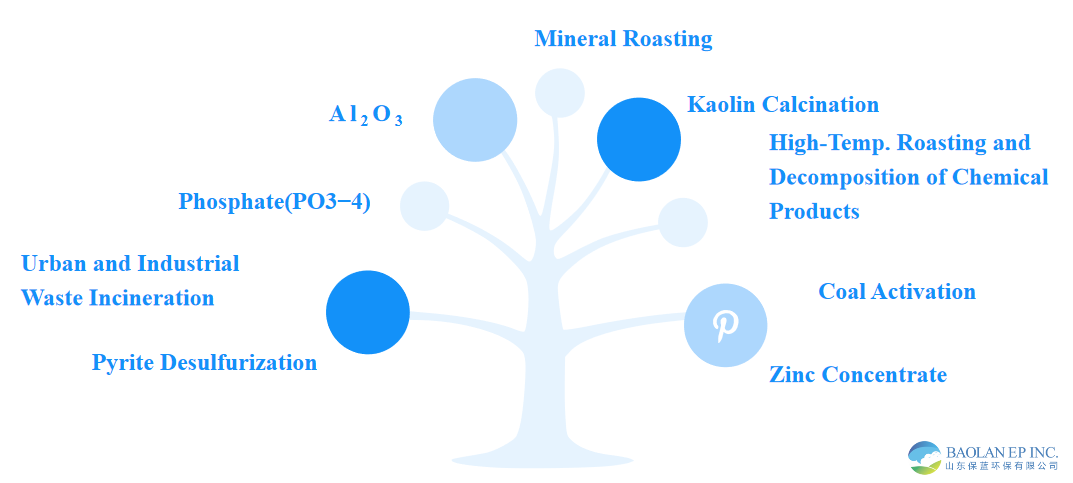
Application