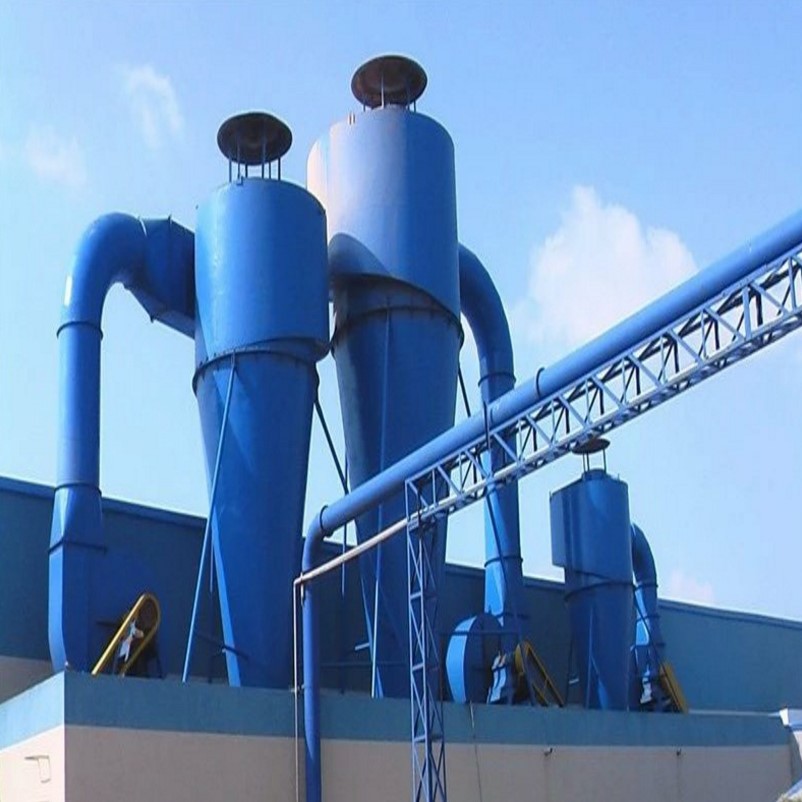
- Incinerator
- Waste Gas Treatment
- Environmental Monitoring
- Product Details
Technology Introduction
Venturi dust removal technology is a highly efficient wet dust removal method that primarily utilizes the special structure of the Venturi tube to achieve the separation of dust and airflow. Below is a detailed introduction to its core principles and characteristics
Basic Structure
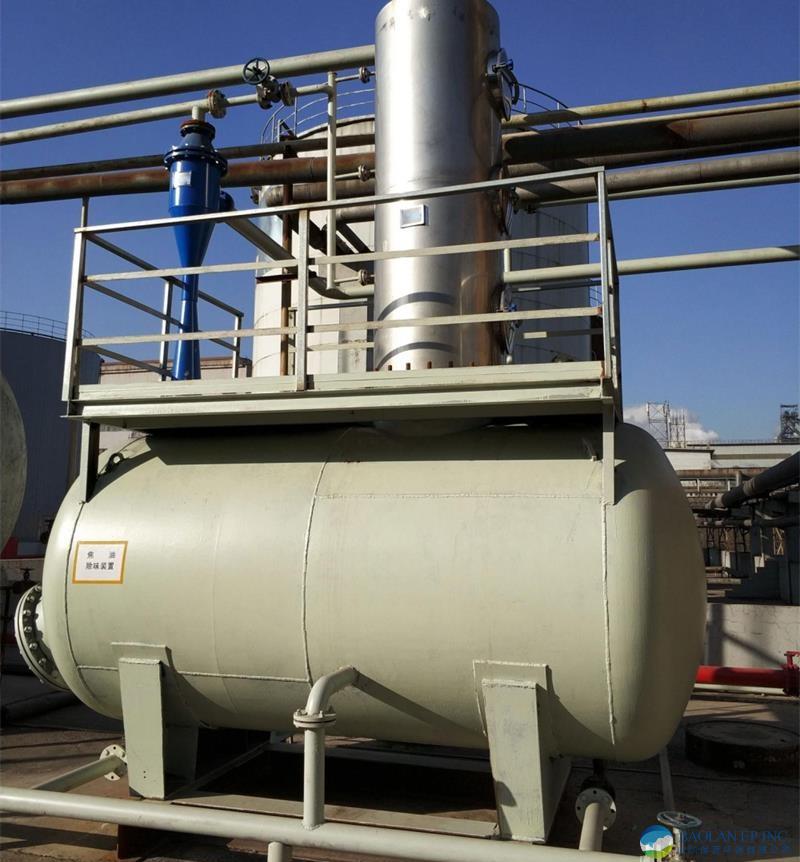
The Venturi dust collector consists of three parts:
Converging section: airflow accelerates, converting pressure energy into kinetic energy.
Throat section: high-speed airflow vigorously mixes with atomized liquid (key functional area).
Diffusing section: kinetic energy is converted back into pressure energy, decelerating to facilitate subsequent separation.
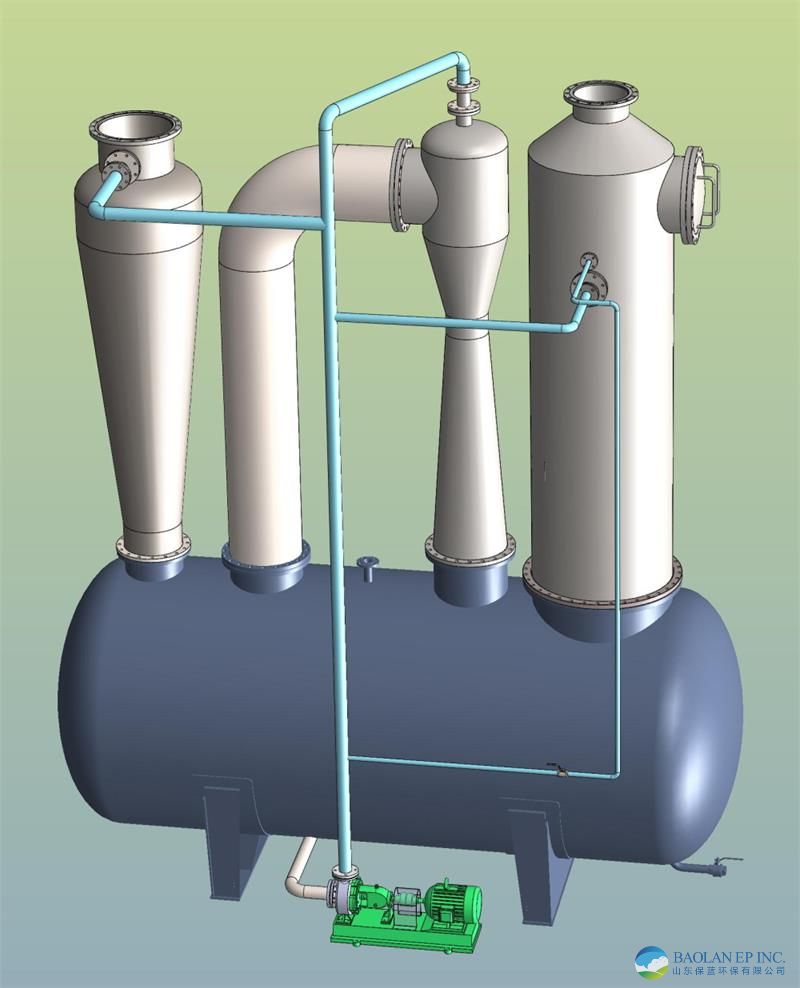
Working Principle
Acceleration and atomization
Dust-laden gas enters the converging section and its velocity sharply increases (up to 60-120 m/s at the throat).
Washing liquid (water or chemical solution) is injected into the throat section, and the high-speed airflow breaks the liquid into tiny droplets.
Dust capture
Droplets combine with dust particles through inertial collision, interception, diffusion, and other effects.
Fine dust (such as PM2.5) adheres to the droplet surfaces due to diffusion effects.
Gas-liquid separation
The mixed airflow enters a cyclone separator or demister, where droplets (containing dust) are separated by centrifugal force or collision.The mixed airflow enters a cyclone separator or demister, where droplets (containing dust) are separated by centrifugal force or collision.
Purified gas is discharged, and wastewater is treated for recycling or discharge.
Technical Features
High-efficiency dust removal: Removal efficiency for 0.1-5μm particles can reach 95%-99%, especially suitable for high concentration dust.
Cooling and absorption: Can simultaneously treat high-temperature waste gas and absorb some gaseous pollutants (such as SO₂).
High pressure loss: High-speed airflow in the throat causes higher energy consumption (requires high-pressure fans).
Strong applicability: Widely used in metallurgy, chemical industry, coal-fired boilers, and other fields.
Key Parameters Affecting Efficiency
Throat velocity: The higher the speed, the better the atomization effect, but the greater the pressure loss.
Liquid-gas ratio (L/G): Usually 0.3-1.5 L/m³; too high will increase operating costs.
Dust characteristics: Hydrophilic dust is easier to capture.
Application Areas
High humidity, high temperature flue gas: such as sintering machines, converter gas purification.
Explosive dust environments: Wet operation reduces explosion risk.
Combined Desulfurization and Denitrification: Achieving synergistic control of multiple pollutants in conjunction with alkaline solution.







